NCERT BOOK CLASS 12TH PHYSICS MCQ
CHAPTER 1 : Electric Charges and Fields
IMPORTANT MCQ
Question 1. What is the SI unit of Electric Charge?
a) Volt
b) Ampere
c) Coulomb
d) Ohm
Answer: c) Coulomb
Question 2. The force between two point charges is given by which law?
a) Ohm’s Law
b) Coulomb’s Law
c) Gauss’s Law
d) Faraday’s Law
Answer: b) Coulomb’s Law
Question 3. What is the unit of Electric Field Intensity?
a) Newton/Coulomb
b) Volt/meter
c) Both a and b
d) Joule/Coulomb
Answer: c) Both a and b
Question 4. What is the charge on an electron?
a) +1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
b) -1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
c) +9.1 × 10⁻³¹ C
d) -9.1 × 10⁻³¹ C
Answer: b) -1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ C
Question 5. What is the SI unit of Electric Flux?
a) Volt-meter
b) Newton-meter²/Coulomb
c) Both a and b
d) Joule-second
Answer: c) Both a and b
Question 6. What is Gauss’s Law related to?
a) Magnetic Field
b) Electric Flux
c) Electric Current
d) Resistance
Answer: b) Electric Flux
Question 7. If the distance between two charges is halved, what happens to the force between them?
a) Halves
b) Doubles
c) Becomes four times
d) Remains the same
Answer: c) Becomes four times
Question 8. What is the Electric Field Intensity in the axial position due to an Electric Dipole?
a) Zero
b) Maximum
c) Minimum
d) Infinite
Answer: b) Maximum
Question 9. The Torque acting on an Electric Dipole placed in a Uniform Electric Field depends on:
a) Charge
b) Dipole Moment
c) Electric Field
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
Question 10. When is the Electric Flux through a closed surface zero?
a) When there is no charge inside the surface
b) When there is a positive charge inside
c) When there is a negative charge inside
d) It is never zero
Answer: a) When there is no charge inside the surface
Question 11. From which type of charge do Electric Field Lines originate?
a) Positive Charge
b) Negative Charge
c) Neutral Charge
d) Magnetic Charge
Answer: a) Positive Charge
Question 12. What is the value of the constant ‘k’ in Coulomb’s Law?
a) 8.85 × 10⁻¹² Nm²/C²
b) 9 × 10⁹ Nm²/C²
c) 6.67 × 10⁻¹¹ Nm²/kg²
d) 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹ Nm²/C²
Answer: b) 9 × 10⁹ Nm²/C²
Question 13. If an object has zero charge, what does it mean?
a) The object has no electrons
b) The number of protons and electrons is equal
c) The object is made only of neutrons
d) The object has no atoms
Answer: b) The number of protons and electrons is equal
Question 14. What does Electric Flux depend on?
a) Magnitude of charge
b) Surface area
c) Angle between field and surface
d) All of the above
Answer: d) All of the above
Question 15. What is the force on a charge ‘q’ in a Uniform Electric Field ‘E’?
a) F = qE
b) F = E/q
c) F = q/E
d) F = q²E
Answer: a) F = qE
Question 16. What is the direction of the Electric Dipole Moment?
a) From negative to positive charge
b) From positive to negative charge
c) Always towards the north
d) Random direction
Answer: b) From positive to negative charge
Question 17. What happens when two like charges are brought close to each other?
a) Attractive force
b) Repulsive force
c) No force
d) Magnetic force
Answer: b) Repulsive force
Question 18. What is Gauss’s Law used to determine?
a) Electric current
b) Electric field
c) Magnetic field
d) Resistance
Answer: b) Electric field
Question 19. Why do Electric Field Lines never intersect?
a) Because energy would be lost
b) Because two directions at a point are not possible
c) Because it’s not a rule
d) Because charge would be destroyed
Answer: b) Because two directions at a point are not possible
Question 20. How many electrons are there in 1 Coulomb of charge?
a) 6.25 × 10¹⁸
b) 1.6 × 10⁻¹⁹
c) 9 × 10⁹
d) 6.02 × 10²³
Answer: a) 6.25 × 10¹⁸
Question 21. What is the net force on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field?
a) Zero
b) qE
c) 2qE
d) qE/2
Answer: a) Zero
Question 22. Electric Field Intensity is a ______ quantity.
a) Scalar
b) Vector
c) Dimensionless
d) Negative
Answer: b) Vector
Question 23. If the Electric Flux through a closed surface is zero, what does it mean?
a) There is no charge inside the surface
b) The positive and negative charges inside are equal
c) Both a and b
d) There is no charge outside the surface
Answer: c) Both a and b
Question 24. Where do Electric Field Lines terminate?
a) Positive Charge
b) Negative Charge
c) Neutral Charge
d) They never terminate
Answer: b) Negative Charge
Question 25. If the distance between two like charges is doubled, what happens to the force between them?
a) Halves
b) One-fourth
c) Doubles
d) Remains the same
Answer: b) One-fourth
Question 26. Which of the following is not a unit of Electric Flux?
a) Nm²/C
b) Vm
c) J/C
d) None
Answer: c) J/C
Question 27. Two charges of 10μC and -20μC are placed 50 cm apart. What is the force between them?
a) Attractive force of 7.2 N
b) Repulsive force of 7.2 N
c) Attractive force of 3.6 N
d) Repulsive force of 3.6 N
Answer: b) Repulsive force of 7.2 N
Question 28. What is the direction of the Electric Field on the equatorial line of an Electric Dipole?
a) Parallel to the dipole moment
b) Opposite to the dipole moment
c) Perpendicular to the dipole moment
d) Random
Answer: b) Opposite to the dipole moment
Question 29. What is the mathematical form of Gauss’s Law?
a) ∮E•dA = q/ε₀
b) ∮B•dA = 0
c) ∮E•dl = -dΦ/dt
d) F = qE
Answer: a) ∮E•dA = q/ε₀
Question 30. When an object is charged by friction, which principle is involved?
a) Charge Conservation
b) Charge Quantization
c) Charge Transfer
d) Charge Distribution
Answer: c) Charge Transfer
Question 31. What is the relationship between Electric Field Intensity (E) and Electric Potential (V)?
a) E = -dV/dr
b) V = -∫E•dr
c) Both a and b
d) No relation
Answer: c) Both a and b
Question 32. 1 Volt/meter (V/m) is equal to:
a) 1 Newton/Coulomb (N/C)
b) 1 Joule/Coulomb (J/C)
c) 1 Volt/Coulomb (V/C)
d) 1 Ohm/meter (Ω/m)
Answer: a) 1 Newton/Coulomb (N/C)
Question 33. What is the Electric Potential at the axial position of an Electric Dipole?
a) Zero
b) Maximum
c) Minimum
d) Infinite
Answer: b) Maximum
Question 34. When a conductor is charged, where does all the charge reside?
a) Uniformly distributed inside the conductor
b) On the surface of the conductor
c) Concentrated at the center
d) At one end of the conductor
Answer: b) On the surface of the conductor
Question 35. Which physical quantity is Gauss’s Law related to in the context of Electric Flux?
a) Electric Field
b) Electric Potential
c) Capacitance
d) Electric Current
Answer: a) Electric Field
Question 36. What is the formula for Torque acting on an Electric Dipole in a Uniform Electric Field?
a) τ = p×E
b) τ = p•E
c) τ = p/E
d) τ = E/p
Answer: a) τ = p×E
Question 37. Which statement about Electric Field Lines is correct?
a) They can intersect each other
b) They always form closed loops
c) They originate from positive charges and terminate at negative charges
d) None of these
Answer: c) They originate from positive charges and terminate at negative charges
Question 38. What is the SI unit of Electric Potential?
a) Volt
b) Newton
c) Joule
d) Coulomb
Answer: a) Volt
Question 39. The Electric Potential due to a Point Charge is inversely proportional to:
a) Square of the charge
b) Distance
c) Square of the distance
d) Charge
Answer: b) Distance
Question 40. The unit of Electric Dipole Moment is:
a) Coulomb-meter (C·m)
b) Coulomb/meter (C/m)
c) Volt-meter (V·m)
d) Newton-meter (N·m)
Answer: a) Coulomb-meter (C·m)
Question 41. If an Electric Dipole is placed at an angle θ in a Uniform Electric Field, what is the torque acting on it?
a) pE sinθ
b) pE cosθ
c) pE tanθ
d) pE cotθ
Answer: a) pE sinθ
Question 42. The density of Electric Field Lines is a measure of:
a) Electric Potential
b) Electric Field Intensity
c) Electric Flux
d) Capacitance
Answer: b) Electric Field Intensity
Question 43. If the Electric Potential at a point is zero, then the Electric Field:
a) Must be zero
b) May or may not be zero
c) Can never be zero
d) Will be infinite
Answer: b) May or may not be zero
Question 44. For which closed surface is the Electric Flux maximum?
a) When the surface encloses maximum charge
b) When the surface area is maximum
c) When there is no charge inside
d) When the surface is a conductor
Answer: a) When the surface encloses maximum charge
Question 45. What is the correct mathematical relationship between Electric Field Intensity (E) and Electric Potential (V)?
a) E = -∇V
b) V = -∫E•dl
c) Both a and b
d) E = ∇×V
Answer: c) Both a and b
Question 46. What is the Electric Potential on the equatorial line of an Electric Dipole?
a) Zero
b) Maximum
c) Minimum
d) Infinite
Answer: a) Zero
Question 47. Electric Field Lines never intersect because:
a) The law of energy conservation must hold
b) The electric field can have only one direction at a point
c) The law of charge conservation must hold
d) All of these
Answer: b) The electric field can have only one direction at a point
Question 48. In an Electrostatic Field, what is the value of ∮E•dl for a closed loop?
a) Zero
b) Infinite
c) The enclosed charge
d) The area of the loop
Answer: a) Zero
Question 49. The Electric Field Intensity at the axial position of an Electric Dipole is inversely proportional to:
a) Distance
b) Square of the distance
c) Cube of the distance
d) Fourth power of the distance
Answer: c) Cube of the distance
Question 50. When applying Gauss’s Law, how is the Gaussian Surface chosen?
a) The shape can be arbitrary
b) The electric field must be constant at every point on the surface
c) The surface must follow symmetry
d) The surface must always be spherical
Answer: c) The surface must follow symmetry
Question 51. Two point charges, +3μC and -4μC, are placed 2 meters apart. What is the magnitude of the force between them? (k = 9×10⁹ Nm²/C²)
a) 27 N
b) 54 N
c) 0.027 N
d) 0.054 N
Answer: c) 0.027 N
Solution:
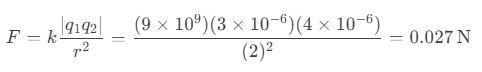
Question 52. A spherical conductor of radius 5 cm has a charge of 10 μC. What is the electric field intensity at its surface?
a) 3.6×10⁷ N/C
b) 1.8×10⁷ N/C
c) 9×10⁶ N/C
d) 4.5×10⁶ N/C
Answer: a) 3.6×10⁷ N/C
Solution:
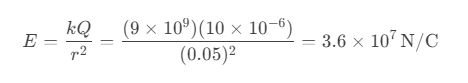
Question 53. An electric dipole with a dipole moment of 6×10⁻⁸ C·m is placed in an electric field of 10⁵ N/C. What is the maximum torque acting on it?
a) 6×10⁻³ Nm
b) 3×10⁻³ Nm
c) 12×10⁻³ Nm
d) 1.5×10⁻³ Nm
Answer: a) 6×10⁻³ Nm
Solution:
τ = pE = (6×10⁻⁸)(10⁵) = 6×10⁻³ Nm
Question 54. A 1 μC charge is placed at the center of a cube with 2 cm sides. What is the electric flux through one face of the cube?
a) 1.88×10⁴ Nm²/C
b) 9.4×10³ Nm²/C
c) 1.13×10⁵ Nm²/C
d) 5.65×10⁴ Nm²/C
Answer: a) 1.88×10⁴ Nm²/C
Solution:
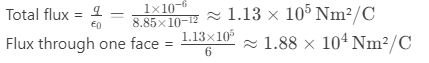
Question 55. A spherical conductor of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 20 cm from its surface is 2×10⁵ N/C, what is the charge?
a) 8.89 μC
b) 4.44 μC
c) 2.22 μC
d) 1.11 μC
Answer: a) 8.89 μC
Solution:
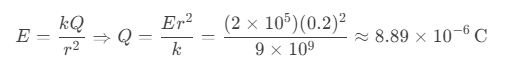
Question 56. Two identical charges of 5 μC are placed 0.1 m apart. What is the electric field intensity at the midpoint?
a) 9×10⁶ N/C
b) 1.8×10⁷ N/C
c) Zero
d) 3.6×10⁷ N/C
Answer: c) Zero
Solution:
The fields due to both charges are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, so the net field is zero.
Question 57. A charge of 8.85 nC is placed at the center of a cube with 2 m sides. What is the electric flux through one face?
a) 100 Nm²/C
b) 167 Nm²/C
c) 200 Nm²/C
d) 333 Nm²/C
Answer: b) 167 Nm²/C
Solution:
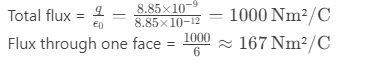
Question 58. What is the electric potential at 1 m from a 1 μC point charge?
a) 9 kV
b) 4.5 kV
c) 18 kV
d) 1 kV
Answer: a) 9 kV
Solution:
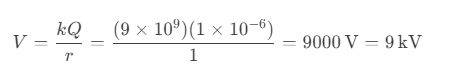
Question 59. A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm is given a 1 μC charge. What is the electric field intensity at 5 cm from its center?
a) 9×10⁵ N/C
b) 1.8×10⁶ N/C
c) Zero
d) 3.6×10⁶ N/C
Answer: c) Zero
Solution:
Inside a conductor, the electric field is zero.
Question 60. Two charges, 2 μC and -5 μC, are placed 0.5 m apart. What is the dipole moment of this system?
a) 3.5×10⁻⁶ C·m
b) 1.0×10⁻⁶ C·m
c) 2.5×10⁻⁶ C·m
d) 7.0×10⁻⁶ C·m
Answer: a) 3.5×10⁻⁶ C·m
Solution:
p = q×2a = (2+5)×10⁻⁶ × 0.25 = 3.5×10⁻⁶ C-m
Question 61. A ring of radius 1 cm has a uniform charge distribution of 10 nC. What will be the electric field intensity at a point 1 cm from the center along its axis?
a) 6.36×10⁴ N/C
b) 3.18×10⁴ N/C
c) 1.59×10⁴ N/C
d) 9.54×10⁴ N/C
Answer: a) 6.36×10⁴ N/C
Solution:
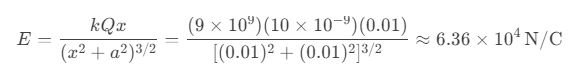
Question 62. Three charges of 2 μC each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 10 cm. What will be the electric potential at the centroid?
a) 540 kV
b) 270 kV
c) 180 kV
d) 90 kV
Answer: a) 540 kV
Solution:
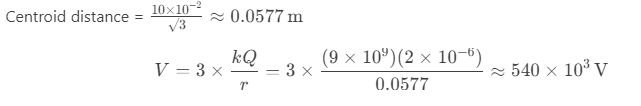
Question 63. A conducting sphere of radius 5 cm is charged to 20 V. What will be the electric field intensity at its surface?
a) 400 V/m
b) 200 V/m
c) 100 V/m
d) 50 V/m
Answer: a) 400 V/m
Solution:
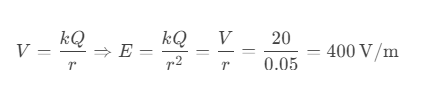
Question 64. Four charges of 1 μC each are placed at the corners of a square of side 1 m. What will be the electric field intensity at the center?
a) 3.6×10⁴ N/C
b) 7.2×10⁴ N/C
c) 1.8×10⁴ N/C
d) Zero
Answer: d) Zero
Solution:
The fields due to all charges at the center are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction, resulting in zero net field.
Question 65. For a point charge of 2 μC, what is the ratio of electric potential to electric field intensity at a distance of 50 cm?
a) 0.5 m
b) 1.0 m
c) 1.5 m
d) 2.0 m
Answer: a) 0.5 m
Solution:
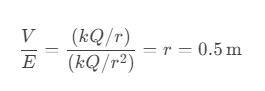
Question 66. A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm is given a charge of 1 μC. What is the electric potential at its surface?
a) 90 kV
b) 45 kV
c) 9 kV
d) 4.5 kV
Answer: a) 90 kV
Solution:
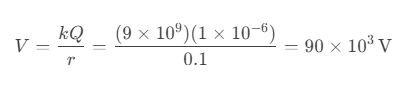
Question 67. Two charges of 5 μC and -3 μC are placed 0.2 m apart. What is the electric potential at the midpoint?
a) 180 kV
b) 90 kV
c) 360 kV
d) 540 kV
Answer: a) 180 kV
Solution:
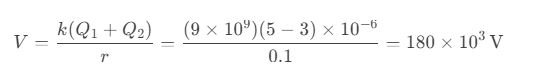
Question 68. A ring of radius 2 cm has a uniform charge distribution of 20 nC. What is the electric field intensity at its center?
a) 4.5×10⁴ N/C
b) 9×10⁴ N/C
c) Zero
d) 1.8×10⁵ N/C
Answer: c) Zero
Solution:
At the center of the ring, the electric fields due to all elements cancel each other out.
Question 69. Two identical charges of 1 μC are placed 1 m apart. What is the electric potential at the midpoint?
a) 18 kV
b) 36 kV
c) 9 kV
d) 4.5 kV
Answer: b) 36 kV
Solution:
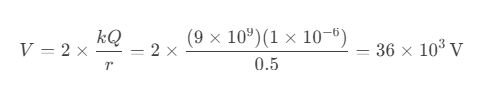
Question 70. A conducting sphere of radius 5 cm is given a charge of 10 nC. What is the electric field intensity at its surface?
a) 3.6×10⁴ N/C
b) 7.2×10⁴ N/C
c) 1.8×10⁴ N/C
d) 9×10⁴ N/C
Answer: a) 3.6×10⁴ N/C
Solution:
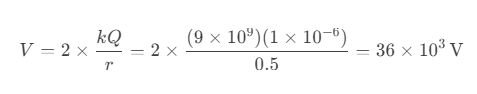
Question 71. Two charges of 1 μC and -2 μC are placed 0.1 m apart. What is the dipole moment of this system?
a) 1×10⁻⁷ C·m
b) 2×10⁻⁷ C·m
c) 3×10⁻⁷ C·m
d) 4×10⁻⁷ C·m
Answer: c) 3×10⁻⁷ C·m
Solution:
p = q×2a = (1+2)×10⁻⁶ × 0.05 = 3×10⁻⁷ C-m
Question 72. A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm is given a charge of 2 μC. What is the electric field intensity at 15 cm from its center?
a) 8×10⁵ N/C
b) 4×10⁵ N/C
c) 2×10⁵ N/C
d) 1×10⁵ N/C
Answer: a) 8×10⁵ N/C
Solution:
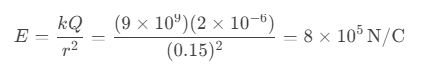
Question 73. A charge of 8.85 pC is placed at the center of a cube of side 1 m. What is the electric flux through one face?
a) 0.167 Nm²/C
b) 1.67 Nm²/C
c) 16.7 Nm²/C
d) 167 Nm²/C
Answer: a) 0.167 Nm²/C
Solution:
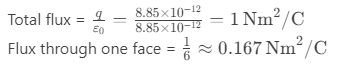
Question 74. For a point charge of 2 μC, what is the ratio of electric potential to electric field intensity at 1 m distance?
a) 0.5 m
b) 1.0 m
c) 1.5 m
d) 2.0 m
Answer: b) 1.0 m
Solution:
V/E = (kQ/r)/(kQ/r²) = r = 1 m
Question 75. A conducting sphere of radius 5 cm is charged to 10 V. What is the electric field intensity at its surface?
a) 100 V/m
b) 200 V/m
c) 300 V/m
d) 400 V/m
Answer: b) 200 V/m
Solution:
E = V/r = 10/0.05 = 200 V/m